“Just about every time, we are building something for the first time,” says Brian O’Connor, the vice president of production operations at Lockheed Martin Space.
Traditionally, aerospace organizations have replied upon thousand-page paper manuals to relay instructions to their workers. In recent years, firms like Boeing and Airbus have started experimenting with augmented reality, but it’s rarely progressed beyond the testing phase. At Lockheed, at least, that’s changing. The firm’s employees are now using AR to do their jobs every single day.
This piece first appeared in our twice-weekly newsletter, Clocking In, which covers how technology is transforming the future of work. Sign up here—it’s free!
Spacecraft technician Decker Jory uses a Microsoft HoloLens headset on a daily basis for his work on Orion, the spacecraft intended to one day sit atop the powerful—and repeatedly delayed—NASA Space Launch System. “At the start of the day, I put on the device to get accustomed to what we will be doing in the morning,” says Jory. He takes the headset off when he is ready to start drilling. For now, the longest he can wear it without it getting uncomfortable or too heavy is about three hours. So he and his team of assemblers use it to learn a task or check the directions in 15-minute increments rather than for a constant feed of instructions.
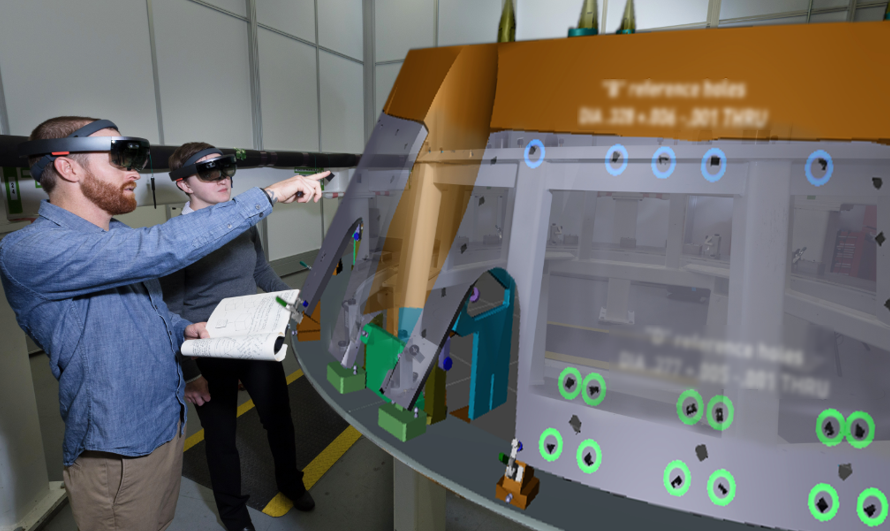
In the headset, the workers can see holograms displaying models that are created through engineering design software from Scope AR. Models of parts and labels are overlaid on already assembled pieces of spacecraft. Information like torquing instructions—how to twist things—can be displayed right on top of the holes to which they are relevant, and workers can see what the finished product will look like.
The virtual models around the workers are even color-coded to the role of the person using the headset. For Jory’s team, which is currently constructing the heat shield skeleton of Orion, the new technology takes the place of a 1,500-page binder full of written work instructions.
Lockheed is expanding its use of augmented reality after seeing some dramatic effects during testing. Technicians needed far less time to get familiar with and prepare for a new task or to understand and perform processes like drilling holes and twisting fasteners.

These results are prompting the organization to expand its ambitions for the headsets: one day it hopes to use them in space. Lockheed Martin’s head of emerging technologies, Shelley Peterson, says the way workers use the headsets back here on Earth gives insight into how augmented reality could help astronauts maintain the spacecraft the firm helped build. “What we want astronauts to be able to do is have maintenance capability that’s much more intuitive than going through text or drawing content,” says Peterson.
For now, these headsets still need some adjustments to increase their wearability and ease of use before they can be used in space. Creating the content the workers see is getting easier, but it still takes a lot of effort. O’Connor sees these as obstacles that can be overcome quickly, though.
“If you were to look five years down the road, I don’t think you will find an efficient manufacturing operation that doesn’t have this type of augmented reality to assist the operators,” he says.
fonte: https://www.technologyreview.com/s/612247/nasa-is-using-hololens-ar-headsets-to-build-its-new-spacecraft-faster/



